Введение
В последнее время я играл с множеством Мандельброта, а это означало, что мне пришлось стряхнуть пыль с памяти о том, как выполнять арифметические действия с комплексными числами. Я создал хороший класс JavaScript, помогающий смазать их. Вот теперь это работает (это довольно сухое объяснение, но я надеюсь, что оно будет полезным).
Быстрое обновление
Когда мы умножаем два числа вместе, результат будет нечетным или четным в зависимости от того, являются ли числа, которые мы умножаем:
-1 * 1 = -1 1 * -1 = -1 1 * 1 = 1 -1 * -1 = 1
Обратите внимание, что возведение в квадрат дает положительное число! Не существует числа, которое можно возвести в квадрат и получить отрицательное число, и здесь в игру вступает мнимое число. Буква i используется для обозначения воображаемого числа, которое при возведении в квадрат равно -1.
i ≔ √(-1) ∴ i² = -1
Это буквально другая числовая линия, точно так же, как у нас есть -2, -1, 0, 1, 2… у нас есть -2i, -1i, 0i, 1i, 2i, 3i….
Комплексное число — это число, состоящее из действительной части и мнимой части. Они записываются в форме a + bi.
Поскольку 0i = 0 числовые линии пересекаются в 0, мы можем изобразить эти числа на графике, обычно ось x — это прямая с действительными числами, а ось y — воображаемая.
Некоторые примеры



Арифметика
Возможно, вы заметили, что комплексные числа очень похожи на векторы, и с той оговоркой, что они i * i = -1 таковыми и являются. Все операции являются обычными векторными операциями, которые корректируются с учетом этого предостережения.
Код
Конструктор класса Complex имеет два параметра.
realimaginary
export class Complex {
constructor(real, imaginary) {
this.real = real;
this.imaginary = imaginary;
}
}
Нуль
Ноль равен 0 + 0i.
/***
* Generate a new <code>Complex(0,0)</code>
* @returns {Complex}
*/
static zero = () => new Complex(0, 0);
нанизывать()
/***
* Returns a string in the form <code>a ± bi</code>.
* @returns {string}
*/
toString() {
const operator = this.imaginary < 0 ? '-' : '+';
return `${this.real} ${operator} ${Math.abs(this.imaginary)}i`;
}
Равно
/***
* Both <i>real</i> and <i>imaginary</i> parts are equal.
* @param other
* @returns {boolean}
*/
equals(other) {
return this.real === other.real && this.imaginary === other.imaginary;
}
Добавлять
add(other) {
return new Complex(
this.real + other.real,
this.imaginary + other.imaginary
);
}
Вычесть
subtract(other) {
return new Complex(
this.real — other.real,
this.imaginary — other.imaginary
);
}
Умножить
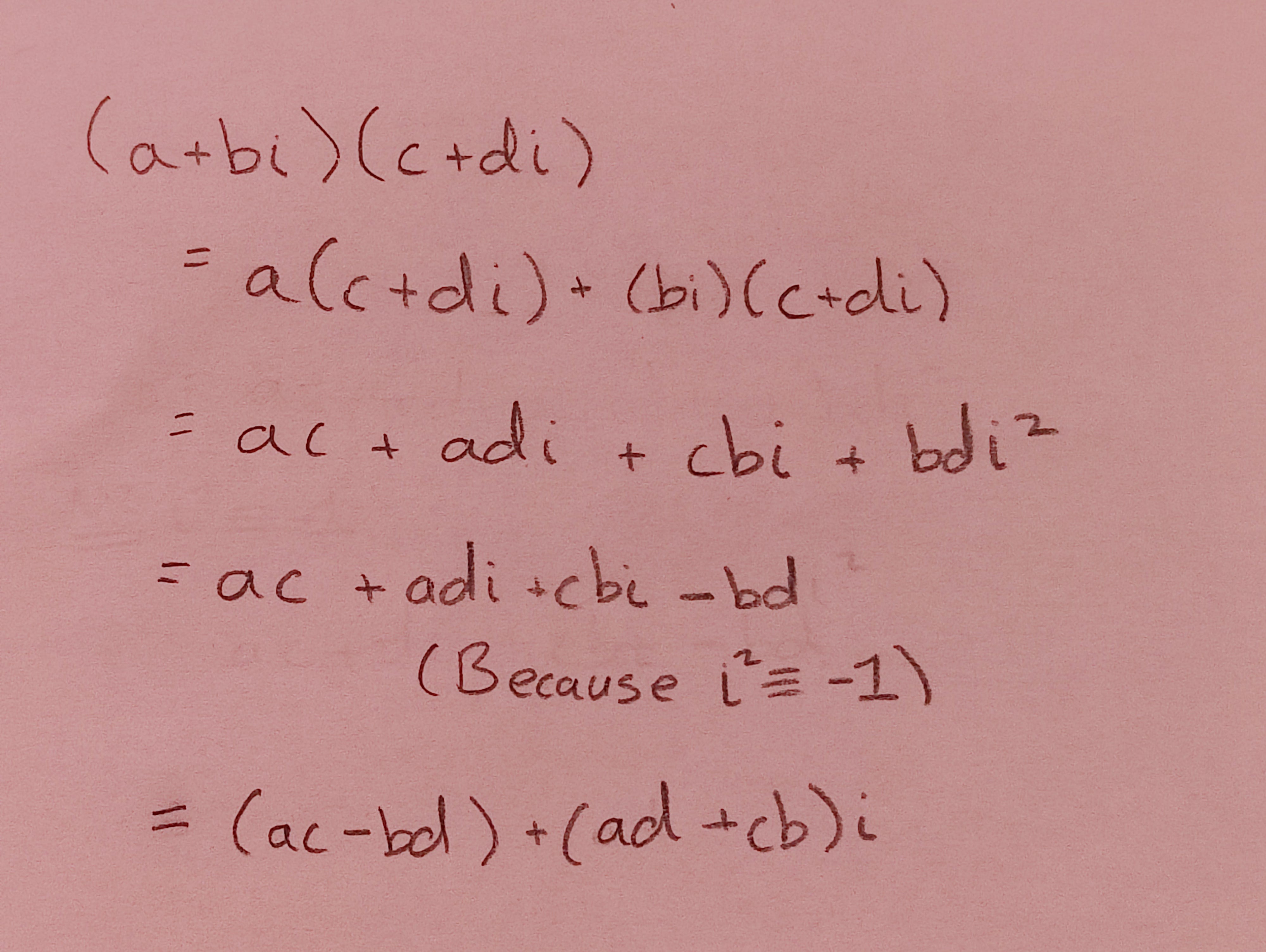
/***
* Multiple this Complex with another.<br/>
* <code>(a + bi)(c + di) = (ac - bd) + (ad + bc)i</code>
* @param other
* @returns {Complex}
*/
multiply(other) {
return new Complex(
this.real * other.real - this.imaginary * other.imaginary,
this.real * other.imaginary + this.imaginary * other.real
);
}
Разделение

/***
* <code>(a + bi) / (c + di) = [(ac + bd) / (c^2 + d^2)] + [(bc - ad) / (c^2 + d^2)]i<code>
* @param other
*/
divide(other) {
const otherMagnitudeSquared =
other.real * other.real + other.imaginary * other.imaginary;
const r =
(this.real * other.real + this.imaginary * other.imaginary) /
otherMagnitudeSquared;
const i =
(this.imaginary * other.real - this.real * other.imaginary) /
otherMagnitudeSquared;
return new Complex(r, i);
}
Полный код
Класс приложения
export class Complex {
constructor(real, imaginary) {
this.real = real;
this.imaginary = imaginary;
}
/***
* Generate a new <code>Complex(0,0)</code>
* @returns {Complex}
*/
static zero = () => new Complex(0, 0);
add(other) {
return new Complex(
this.real + other.real,
this.imaginary + other.imaginary
);
}
subtract(other) {
return new Complex(
this.real - other.real,
this.imaginary - other.imaginary
);
}
/***
* Multiple this Complex with another.<br/>
* <code>(a + bi)(c + di) = (ac - bd) + (ad + bc)i</code>
* @param other
* @returns {Complex}
*/
multiply(other) {
return new Complex(
this.real * other.real - this.imaginary * other.imaginary,
this.real * other.imaginary + this.imaginary * other.real
);
}
/***
* <code>(a + bi) / (c + di) = [(ac + bd) / (c^2 + d^2)] + [(bc - ad) / (c^2 + d^2)]i<code>
* @param other
*/
divide(other) {
const otherMagnitudeSquared =
other.real * other.real + other.imaginary * other.imaginary;
const r =
(this.real * other.real + this.imaginary * other.imaginary) /
otherMagnitudeSquared;
const i =
(this.imaginary * other.real - this.real * other.imaginary) /
otherMagnitudeSquared;
return new Complex(r, i);
}
magnitude() {
return Math.sqrt(
this.real * this.real + this.imaginary * this.imaginary
);
}
/***
* Returns a string in the form <code>a ± bi</code>.
* @returns {string}
*/
toString() {
const operator = this.imaginary < 0 ? '-' : '+';
return `${this.real} ${operator} ${Math.abs(this.imaginary)}i`;
}
/***
* Both <i>real</i> and <i>imaginary</i> parts are equal.
* @param other
* @returns {boolean}
*/
equals(other) {
return this.real === other.real && this.imaginary === other.imaginary;
}
}
Тестовые случаи
Здесь используется Витест.
import { describe, it, expect } from 'vitest';
import { Complex } from './Complex.js';
describe('Calling zero()', () => {
const zero = Complex.zero();
it('should return 0 real part', () => {
expect(zero.real).toBe(0);
});
it('should return 0 imaginary part', () => {
expect(zero.imaginary).toBe(0);
});
});
describe('Creating a new number', () => {
const expectedReal = Math.random();
const expectedImaginary = Math.random();
const actual = new Complex(expectedReal, expectedImaginary);
it(`should return the expected real part (${expectedReal})`, () => {
expect(actual.real).toBe(expectedReal);
});
it(`should return the expected imaginary part (${expectedImaginary})`, () => {
expect(actual.imaginary).toBe(expectedImaginary);
});
});
it('Should correctly calculate the magnitude', () => {
const dummyReal = Math.random();
const dummyImaginary = Math.random();
const expected = Math.sqrt(
dummyReal * dummyReal + dummyImaginary * dummyImaginary
);
const actual = new Complex(dummyReal, dummyImaginary).magnitude();
console.dir({ dummyReal, dummyImaginary, actual, expected });
expect(actual).toBe(expected);
});
describe('Equality', () => {
it('should return true when equal', () => {
const complex1 = new Complex(Math.random(), Math.random());
const complex2 = new Complex(complex1.real, complex1.imaginary);
const actual = complex1.equals(complex2);
expect(actual).toBe(true);
});
it('should return false when real part differs', () => {
const complex1 = new Complex(Math.random(), Math.random());
const complex2 = new Complex(complex1.real + 1, complex1.imaginary);
const actual = complex1.equals(complex2);
expect(actual).toBe(false);
});
it('should return true when equal', () => {
const complex1 = new Complex(Math.random(), Math.random());
const complex2 = new Complex(complex1.real, complex1.imaginary + 1);
const actual = complex1.equals(complex2);
expect(actual).toBe(false);
});
});
describe('Arithmetic', () => {
const complex1 = new Complex(6, 3);
const complex2 = new Complex(7, -5);
describe('Add', () => {
const expectedReal = complex1.real + complex2.real;
const expectedImaginary = complex1.imaginary + complex2.imaginary;
const actual = complex1.add(complex2);
it(`Real part should be ${expectedReal}`, () => {
expect(actual.real).toBe(expectedReal);
});
it(`Imaginary part should be ${expectedImaginary}`, () => {
expect(actual.imaginary).toBe(expectedImaginary);
});
});
describe('Subtract', () => {
const expectedReal = complex1.real - complex2.real;
const expectedImaginary = complex1.imaginary - complex2.imaginary;
const actual = complex1.subtract(complex2);
it(`Real part should be ${expectedReal}`, () => {
expect(actual.real).toBe(expectedReal);
});
it(`Imaginary part should be ${expectedImaginary}`, () => {
expect(actual.imaginary).toBe(expectedImaginary);
});
});
describe('Multiply', () => {
const expectedReal = complex1.real + complex2.real;
const expectedImaginary = complex1.imaginary + complex2.imaginary;
const actual = complex1.add(complex2);
it(`Real part should be ${expectedReal}`, () => {
expect(actual.real).toBe(expectedReal);
});
it(`Imaginary part should be ${expectedImaginary}`, () => {
expect(actual.imaginary).toBe(expectedImaginary);
});
});
describe('Divide', () => {
const expectedReal = 27 / 74;
const expectedImaginary = 51 / 74;
const actual = complex1.divide(complex2);
it(`should have correct real`, () => {
expect(actual.real).toBe(expectedReal);
});
it(`should have correct imaginary`, () => {
expect(actual.imaginary).toBe(expectedImaginary);
});
});
});
describe('toString()', () => {
it('for positive imaginary part', () => {
const dummyReal = 1;
const dummyImaginary = 1;
const expected = `${dummyReal} + ${dummyImaginary}i`;
const actual = new Complex(dummyReal, dummyImaginary).toString();
expect(actual).toBe(expected);
});
it('for zero imaginary part', () => {
const dummyReal = 1;
const dummyImaginary = 0;
const expected = `${dummyReal} + ${dummyImaginary}i`;
const actual = new Complex(dummyReal, dummyImaginary).toString();
expect(actual).toBe(expected);
});
it('for negative imaginary part', () => {
const dummyReal = 1;
const dummyImaginary = -1;
const expected = `${dummyReal} - ${Math.abs(dummyImaginary)}i`;
const actual = new Complex(dummyReal, dummyImaginary).toString();
expect(actual).toBe(expected);
});
});
Заключение
Должен признаться, было довольно весело заново открывать для себя эти выводы, я давно не занимался векторной математикой.
Это была не совсем захватывающая статья, она очень сухая, но функции важны, если вы хотите поиграть с множествами Мандельброта или Жюлиа или с чем-то, что требует комплексных чисел.
Спасибо за прочтение.